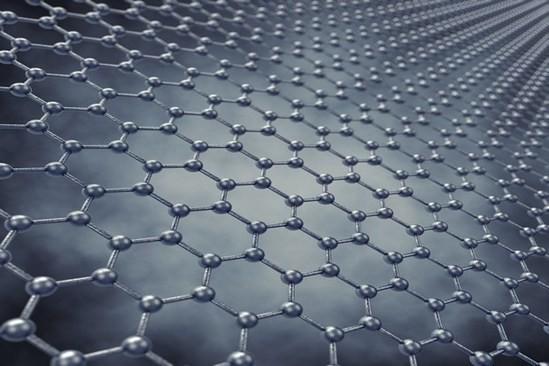
Graphene, a type of carbon nanotube, is a fascinating material with unique properties that have applications in a variety of fields, including electronics, medicine, and energy. Graphene is made from single layers of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice structure.
(where is graphene found)
One of the most well-known sources of graphene is from diamond. Diamond is a highly stable and chemically inert material that can be cleaved into thin films by high-energy laser radiation. The diamond films are then cleaved again to form graphene nanoribbons. This process, known as “diamond cleavage,” creates small but very strong films of graphene that can be easily extracted and purified.
Another source of graphene is from graphite. Graphite is a two-dimensional material that has been used for centuries as a building material due to its strength, flexibility, and insulating properties. Graphite flakes are then cut and peeled to form graphene nanoribbons. Like diamond, this process also creates small but very strong films of graphene that can be easily extracted and purified.
In addition to these direct sources of graphene, there are also indirect sources of graphene. One indirect source of graphene is from biomass, such as agricultural waste and food waste. These materials contain carbon dioxide, which can be converted into glucose using an enzyme called celluloseases. The glucose can then be used to produce chemicals, including graphene, through chemical reactions.
Another indirect source of graphene is from foams. Metal foams are formed by mixing metal powders with a liquid matrix, such as water or ethanol. When the mixture is heated and dried, it forms a foam that contains a layer of metal particles. As the metal particles grow and spread throughout the foam, they create a network of interconnected sheets of metal that can be rolled up to form graphene nanoribbons.
Graphene has a number of potential applications across a wide range of fields. It is incredibly lightweight and strong, making it a good candidate for use in aerospace and automotive industries. It is also highly transparent and conductive, making it ideal for use in electronics and sensors. Additionally, graphene has many promising applications in medicine, such as as a potential treatment for cancer and inflammation.
(where is graphene found)
Overall, graphene is a fascinating material with a wide range of potential applications. Its unique properties make it an attractive choice for researchers and engineers looking to develop new technologies and materials. While more research is needed to fully understand the properties of graphene and its potential uses, it is clear that this material will continue to play a significant role in the development of cutting-edge technologies in the years to come.
Inquiry us