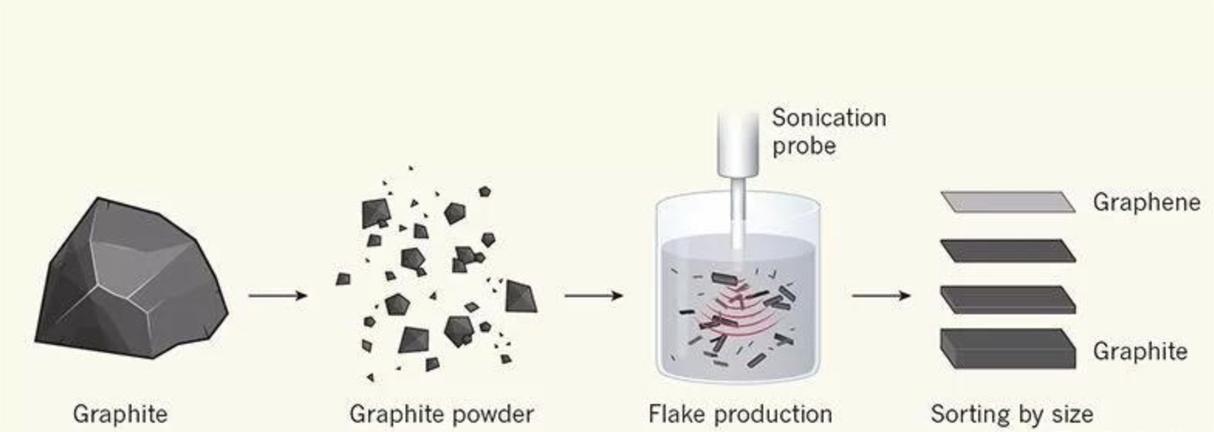
Graphene is a two-dimensional material that has gained significant attention for its unique properties as a carrier material for electronic devices. One of the key features of graphene is its incredibly high electron mobility, which allows it to carry electric charge with incredible speed.
(how fast are electrons moving in graphene)
The concept of electron mobility refers to the rate at which an electron moves through a material. In general, the greater the mobility of an electron, the faster it can move. Graphene is particularly well-suited for high-speed electronic applications due to its exceptional electronic properties.
One of the most important aspects of electron mobility is the presence of spicular lattice structure within graphene. Spicular lattices consist of graphene atoms arranged in parallel rows and columns. The spacing between these rows and columns is much smaller than the distance between atoms, allowing for increased electron mobility.
In addition to the spicular lattice structure, graphene also exhibits unique electronic properties such as its high thermal conductivity and strong covalent bonding. These properties make graphene a promising candidate for use in high-speed electronic devices.
To further illustrate the importance of electron mobility in graphene, consider a simple model of a single graphene atom. Atoms in graphene are defined by their position along the x and y axes, and their spin direction is determined by the orientation of their carbon-carbon bonds.
Assuming that the spins of all atoms in a sheet of graphene are aligned parallel to each other, we can calculate the average spin direction of the entire sheet using quantum mechanics. This calculation shows that the average spin direction of the entire sheet is perpendicular to the graphene plane, indicating that electrons are moving in a transverse direction along the z-axis.
However, this is only one aspect of electron mobility in graphene. By increasing the number of layers in a graphene sheet, we can create a more complex system where different layers have different spin directions and therefore exhibit different levels of electron mobility.
(how fast are electrons moving in graphene)
Overall, the high electron mobility in graphene is a key factor driving its potential as a high-speed electronic device. As researchers continue to study the properties of graphene, we can expect to see even more innovative uses for this revolutionary material.
Inquiry us