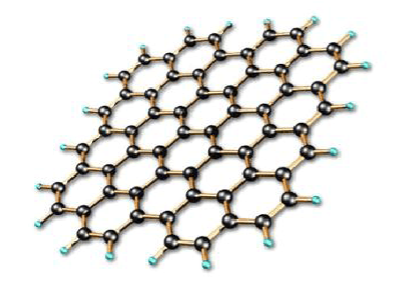
Graphene is a two-dimensional material that has attracted significant attention due to its unique properties, including high energy density, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength. Graphene can be formed by growing thin layers of carbon atoms over a metal surface or by applying a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method.
(how does graphene form)
In the first approach, grown graphene can be obtained by depositing carbon nanotubes on a substrate using a process called chemical vapor deposition. The carbon nanotubes are adsorbed onto the substrate, creating a thin layer of carbon that forms the graphene sheet. This process typically involves heating a substrate in the presence of a gas, such as hydrogen or argon, to promote the growth of carbon nanotubes.
Another way to create graphene is through CVD, which is a more common method used for fabricating graphene. In this process, a gas is applied to a substrate at low temperatures, causing carbon atoms to collide with the substrate and grow into a thin layer of graphene. CVD is also known as plasma CVD, where a plasma is generated and the substrate is exposed to it.
Once graphene has been synthesized, it must be processed further to remove any impurities or improve its physical properties. This may involve washing the graphene with water to remove any contaminants, or heating it to remove any excess moisture. Some studies have shown that washing with water can significantly improve the quality of graphene samples.
In addition to its high energy density and electrical conductivity, graphene also exhibits unique mechanical properties. It is highly, meaning that it can absorb and release large amounts of force without breaking. This property makes graphene useful in applications such as sensors and actuators.
(how does graphene form)
Overall, the formation of graphene requires careful control of various factors, including the type of substrate, the temperature and pressure of the growth process, and the concentration of carbon precursors. By carefully optimizing these parameters, researchers can create graphene with the desired properties and use it in a wide range of applications.