Copper and graphene are two materials that have shown great potential in making high-performance blades for various purposes. Copper is known for its strength, durability, and low maintenance requirements, while graphene is a highly conductive material that can increase the performance of cutting tools.
(can copper and graphene make a durable blade)
One of the key advantages of using copper as a blade material is its exceptional strength. Copper has a high tensile strength and can withstand significant stresses without breaking or wearing down quickly. This makes it ideal for use in demanding applications where precision and stability are essential. Additionally, copper can be easily machined and polished to produce a sharp edge, which reduces friction and ensures optimal performance.
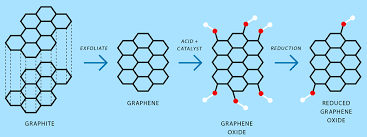
Graphene, on the other hand, is an incredibly strong and lightweight material that can significantly improve the performance of cutting tools. Graphene is made up of carbon atoms arranged in a unique way that gives it a very high electrical conductivity. This means that electricity can flow through the graphene matrix more easily than with traditional metals, resulting in faster cutting speeds and better edge control.
Furthermore, graphene has a lower surface area-to-volume ratio compared to traditional metals, which means that it requires less maintenance and energy to operate. This means that cutting tools made from graphene can be operated at higher temperatures and pressures without suffering from overheating or fatigue.
In addition to its strength and durability, copper also has many benefits over traditional blade materials. For example, copper is non-reactive to most chemicals, making it safe to use in harsh environments. It is also corrosion-resistant, meaning that it can last for years without losing its properties.
However, one potential drawback of using copper as a blade material is that it is relatively expensive. Copper is a difficult metal to work with, requiring specialized equipment and techniques to remove the underlying surface layer. This can make it more expensive to manufacture and install cutting tools than those made from other materials.
Graphene, on the other hand, is generally much cheaper to produce than copper. The cost of producing graphene depends on the scale of production, but even small quantities can be relatively inexpensive. Furthermore, once the graphene blades are produced, they can be manufactured using standard manufacturing processes, which can reduce their overall cost.
Despite these advantages, the choice between copper and graphene as a blade material still comes down to specific application requirements. For example, if the blades will be used in harsh environments, such as extreme temperatures or chemical exposure, then copper may be the better choice. However, if the blades will be used in more general-purpose applications, such as food processing or scientific research, then graphene may be the better choice due to its superior performance and lower cost.
(can copper and graphene make a durable blade)
In conclusion, copper and graphene have both shown promise as high-performance blade materials. While copper is known for its strength and durability, graphene has the potential to significantly improve the performance of cutting tools by increasing their speed, edge control, and reliability. As these technologies continue to advance, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of copper and graphene-based blades in a range of industries.
Inquiry us