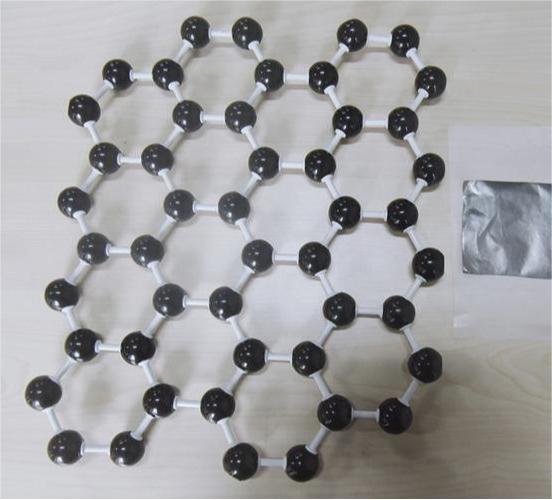
Graphene is an incredibly promising material with many potential applications in fields such as electronics, energy storage, and biotechnology. However, it can be difficult to produce graphene on a large scale without using chemicals or other manufacturing processes that can be hazardous to human health and the environment.
(can you make your own graphene)
One way to create graphene on a larger scale is through a process called chemical vapor deposition (CVD). CVD involves heating a substrate to high temperatures in the presence of gases, which causes the atoms in the substrate to condense and form a layer of graphene on top. This process is typically carried out using specialized equipment that can control the temperature, pressure, and composition of the gas mixture used for CVD.
There are several factors that affect the quality and properties of graphene produced through CVD, including the quality of the graphene substrate, the composition of the gas mixture used, and the conditions under which the graphene is grown. To improve the yield and quality of graphene produced through CVD, researchers are constantly working to optimize these parameters.
Another method for creating graphene on a large scale is through mechanical exfoliation. Mechanical exfoliation involves removing layers of graphene from a pre-grown graphene sheet using mechanical force. This process can be carried out using a variety of tools and techniques, including、、.
The properties of graphene differ significantly from those of its precursors, including carbonaceous materials such as graphite. Graphene has a highly conductive surface area, making it an excellent material for use in electronic devices such as transistors and sensors. It also has strong electrical stability and is resistant to degradation over time.
Despite its promising potential, graphene faces many challenges when it comes to widespread commercialization. For example, the production of graphene requires significant amounts of resources, including rare metals and valuable chemicals, and the process can be expensive and time-consuming. Additionally, graphene has a low thermal conductivity, which means that it requires a lot of heat to maintain its electrical properties.
To address these challenges, researchers are working on developing new methods for producing graphene that are more efficient and cost-effective. One approach is to explore the use of nanomaterials such as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and nanoscale porous structures to confine and support the growth of graphene.
Another approach is to develop new synthesis methods for producing graphene at a larger scale. For example, researchers have been exploring the use of micro-scale electrochemical systems to produce graphene directly on surfaces.
(can you make your own graphene)
Overall, while graphene faces many challenges when it comes to widespread commercialization, there is still much to be learned about this promising material. As research in this field continues to advance, we may see even more innovative uses for graphene in the future.
Inquiry us