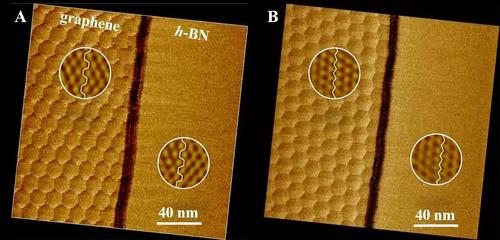
Graphene is a two-dimensional material that was discovered in 2004 by scientists at the University of Amsterdam. Since then, its properties have been extensively studied and its potential applications have become increasingly popular.
(how has graphene advanced)
One of the key advantages of graphene is its high surface area, which allows it to act as a conductor for electricity. This means that it can be used to create electronic devices such as sensors, memory chips, and power electronics. Graphene can also be used as a fuel cell, as it has the highest theoretical efficiency among all known materials.
Another important property of graphene is its exceptional strength and stiffness. It can be made into flexible conductive films and sheets that can be used to build strong, lightweight structures. This makes graphene an ideal material for use in the aerospace industry, where strong materials are needed for structural components.
In addition to its practical uses, graphene has also been found to have potential applications in the field of medicine. One promising application is in the development of new drugs, as the unique properties of graphene make it well-suited for drug delivery systems. Graphene can also be used to create new types of medical implants, such as biodegradable balloons that release drugs over time.
Graphene has also gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential applications in renewable energy. One of the most promising applications of graphene is in the creation of new types of solar cells, as its high surface area and electrical conductivity make it well-suited for this purpose. Researchers are also working on using graphene to develop new types of batteries, as its high energy density and long cycle life make it well-suited for this purpose.
Despite its many potential benefits, there are still some challenges associated with the use of graphene. For example, the process of creating graphene from flakes of individual atoms is complex and requires specialized equipment. Additionally, graphene can be difficult to work with due to its low melting point and high reactivity, which can cause problems during processing.
(how has graphene advanced)
Despite these challenges, graphene has shown great promise as a material with many potential applications. As research continues to advance, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the field of graphene and its potential applications in the future.
Inquiry us