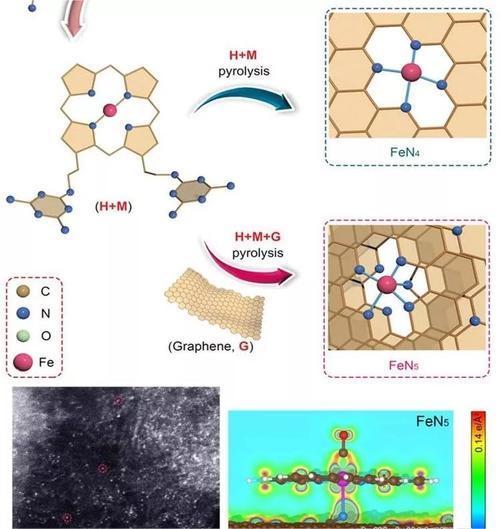
Graphene Federated Exchanges (GFEs) are a type of transistors that operate on a decentralized network, allowing multiple devices to communicate and share data simultaneously. One important aspect ofGFEs is their ability to modulate the flow of information, meaning that they can control how much data is sent or received by each device.
(how is n modulated in a graphene fet)
One way in whichGFEs modulate information is through the use of phase shifter gates. These gates allow the device to manipulate the phase of electrical signals, which can have an impact on the amount of information being transmitted. By controlling the phase of the signals,GFEs can ensure that only certain bits are transmitted at any given time, effectively selecting and prioritizing data for transmission.
In addition to phase shifters,GFEs also use other techniques to modulate information. For example, they may use amplifyers to amplify specific bits of information before transmitting them, or they may use filters to remove noise from the signals before transmitting them.
It’s worth noting thatGFEs can also be designed to take advantage of other properties of graphene, such as its high electron mobility and low resistance. For example, the high mobility of electrons in graphene means that they can move quickly through the device, allowing for faster data transfer and higher throughput. Additionally, the low resistance of graphene means that it can carry more current without losing energy.
(how is n modulated in a graphene fet)
Overall,GFEs represent a promising new technology for enabling communication on decentralized networks. By using various techniques to modulate the flow of information, these devices can significantly increase their speed and efficiency, making them well-suited for applications such as sensor networks, IoT devices, and other types of distributed systems. As researchers continue to explore the potential ofGFEs, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in this field.
Inquiry us