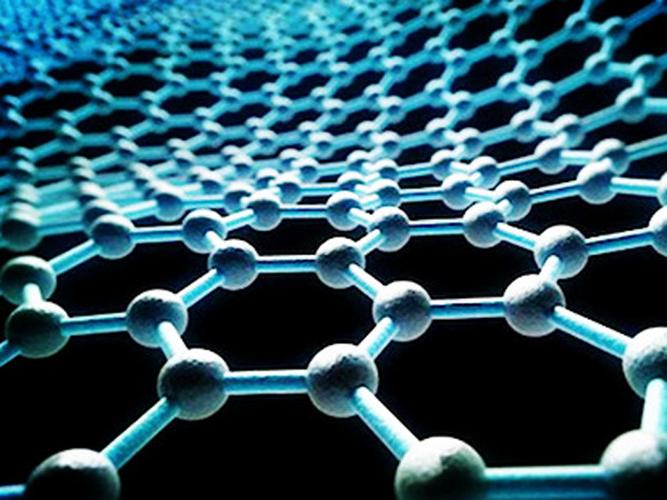
Graphene, a type of two-dimensional material with unique properties, has been making waves in recent years due to its potential applications in a variety of fields, including electronics, energy storage, and biotechnology.
(how many inches thick is graphene)
One of the most well-known uses of graphene is as an insulator, which means it can effectively block electrical current flow without losing its electrical conductivity. This makes it useful for creating electronic devices that require low-power operations, such as solar cells and batteries.
Another application of graphene is as a conductor, which means it can carry electricity with minimal resistance. Graphene is also used in energy storage systems, where it can store large amounts of energy without being depleted over time.
Graphene is also used in medicine and materials science, among other areas. For example, graphene-based sensors have been developed to detect small changes in the levels of specific molecules in the body, which could be useful for diagnosing diseases.
The thickness of graphene depends on several factors, including the purity of the material, the temperature at which it is synthesized, and the conditions under which it is used. Generally speaking, graphene is less dense than most other materials, so it can be made thinner by increasing the number of layers.
In order to create a thin layer of graphene, scientists typically use chemical vapor deposition (CVD) techniques. CVD involves heating a gas mixture to high temperatures and exposing it to a substrate. The substrate is then covered with a layer of carbon dioxide gas, which creates a monolayer of graphene when enough heat is applied.
Once a thin layer of graphene is created, it can be further optimized by varying the conditions of synthesis, such as temperature and pressure. This can result in different structures and properties of the material, depending on how it is handled during the process.
(how many inches thick is graphene)
Overall, the thickness of graphene depends on a complex interplay between the composition of the material, the method of synthesis, and the specific conditions under which it is used. While there is still much research to be done in this field,(graphene technology is rapidly growing around the world) it has the potential to revolutionize a wide range of industries and transform the way we think about materials and energy.
Inquiry us