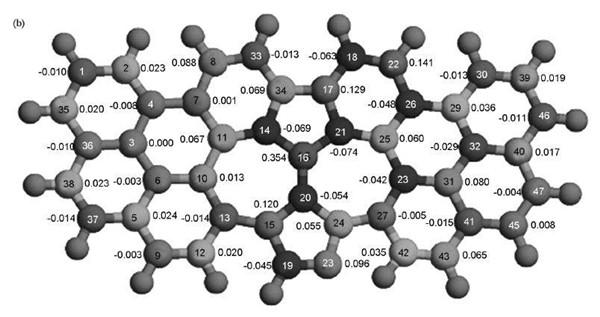
Graphene is a highly conductive material that has gained popularity as a new computing material in recent years. It is made up of carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional honeycomb lattice structure, giving it unique electronic properties such as high conductivity and thermal conductivity.
(how much heat would a graphene cpu generate)
The question of how much heat a graphene CPU generates is an interesting one, as it has important implications for the energy efficiency and sustainability of modern computing systems. One way to estimate the heat generated by a graphene CPU would be to measure its electrical resistance at different temperatures.
For example, if we were to place a graphene CPU on a cold surface, its electrical resistance would be relatively low, as it has low thermal conductivity. As we increase the temperature of the CPU, its electrical resistance would rise, leading to an increase in power consumption and potentially causing damage to the hardware. This is why many researchers and developers are exploring alternative cooling solutions for graphene-based devices.
Another way to estimate the heat generated by a graphene CPU would be to measure its thermal conductivity. Thermal conductivity is a measure of how easily heat moves through a material, and it can vary depending on the composition and arrangement of the atoms in a material. Graphene has been shown to have high thermal conductivity, which means that it is able to transfer heat more efficiently than other materials.
(how much heat would a graphene cpu generate)
Overall, while there is still much research to be done in this area, it is clear that graphene-based computing devices have the potential to provide significant benefits over traditional computing technologies. By optimizing their design and manufacturing processes, we may be able to create CPUs that are more efficient, durable, and sustainable than current alternatives.
Inquiry us