Single-Layer Graphene: A Versatile Material for Electronic and Biomedical Applications
(how to confirm single layered graphene using raman shift)
Introduction:
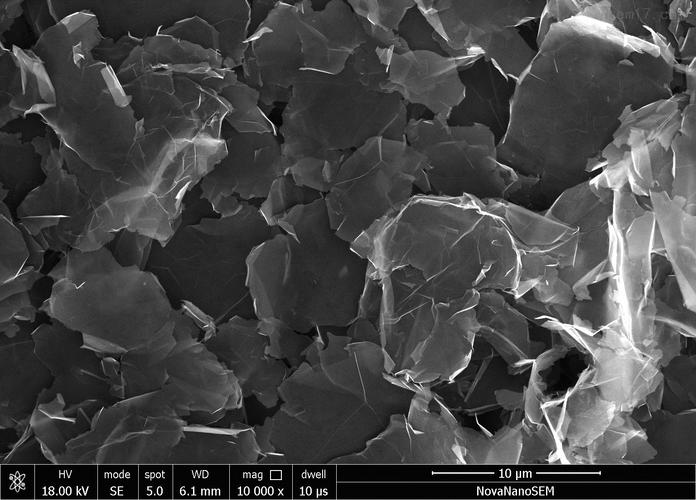
Graphene, a two-dimensional atomic layer material, has attracted immense interest due to its unique properties such as high electrical conductivity, strength, and thermal stability. Single-layer graphene is an excellent material for electronic applications due to its excellent conductivity, but it is also highly sensitive to external factors like temperature, humidity, and pressure. To confirm that a sample contains a single layer graphene, one can use Raman spectroscopy, which provides information about the vibrational modes of atoms in a material. This method can be used to confirm single-layer graphene without any prior knowledge of the material’s structure.
Methodology:
Raman spectroscopy is based on the interaction between light and matter. When light interacts with a surface or material, it produces vibrations that are detected by a spectrometer. The absorption of light by a molecule causes the molecules to vibrate, creating a spectrum of frequencies that depends on the type and number of vibrational modes present. In the case of single-layer graphene, Raman spectroscopy provides information about the vibrational modes of the atoms in the graphene sheet. By measuring the Raman spectra of different samples containing single-layer graphene, one can determine if there is a single layer graphene present.
Sample Preparation:
To prepare a sample for Raman spectroscopy, the graphene sheet must be sliced into thin slices and mounted on a substrate. The substrate can be anything from glass to metal. Once the sample is prepared, it must be illuminated with a laser beam. The intensity of the laser beam should be controlled to ensure that only the top layer of graphene is exposed to the light. The laser intensity and frequency must be adjusted to match the characteristics of the graphene sheet being analyzed.
Data Collection:
The data collected during Raman spectroscopy is analyzed using specialized software tools called Raman Spectroscopy Software (RSS). RSS analyzes the data collected from the Raman experiment and identifies the vibrational frequencies present in the graphene sheet. The software then calculates the intensity of each vibrational mode and compares it to the reference intensity for the same vibrational mode.
Conclusion:
(how to confirm single layered graphene using raman shift)
In conclusion, Raman spectroscopy can be used to confirm the presence of single-layer graphene in a material without any prior knowledge of the material’s structure. By preparing a sample with a thin graphene layer and illuminating it with a laser beam, RSS can identify the vibrational frequencies present in the graphene sheet and determine if there is a single layer graphene present. With this method, researchers can confirm the existence of single-layer graphene in various materials without having to perform extensive structural analysis of the samples. Further research could explore the potential applications of single-layer graphene and optimize its synthesis methods for practical applications.
Inquiry us