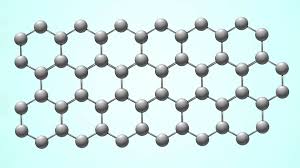
Graphene is a highly conducting, lightweight, and durable material that has revolutionized the field of electronics, energy storage, and biomedical engineering. Graphene is made up of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, which gives it unique electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties.
(how to make graphite into graphene)
There are several ways to produce graphene from graphite, but one of the most efficient methods is through chemical vapor deposition (CVD). CVD involves exposing a solid surface to a gaseous carrier, such as hydrogen or nitrogen, at high temperatures and pressures. The carrier diffuses across the surface, creating a layer of graphene on top of the existing material.
To make graphene out of graphite, you will need the following equipment:
* A high-pressure torch or laser cutter
* A substrate, such as silicon wafer or glass slide
* An organic solvent, such as methanol or acetone
* An etchant, such as hydrogen peroxide or phosphoric acid
* Carbon sources, such as graphite powder or graphite flakes
The first step in CVD is to prepare the substrate by removing impurities and roughening the surface. Then, a liquid solution containing carbon sources and an organic solvent is applied to the substrate and left to react for several hours at high temperatures, typically between 3000°C and 6000°C. The reaction produces carbon nanosheets or flakes, which can be separated from the matrix by centrifugation.
Once you have obtained the graphene samples, they can be processed further to refine their properties. For example, use electron beam etching to remove unwanted materials and smooth the surface, or perform chemical functionalization to introduce specific properties, such as or durability.
Graphene has many potential applications, including in electronics, energy storage, and medicine. It is highly conductive and lightweight, making it ideal for use in power electronics and microwave circuits. Its strong magnetic properties make it suitable for use in superconducting magnets, while its high mechanical strength makes it useful for structural components.
Graphene has also been shown to have exceptional temperature stability and low toxicity, making it safe for use in a variety of applications. However, there are still some challenges to overcome before graphene can become widely used in industry, such as scalability issues and difficulty in achieving high-quality graphene production.
(how to make graphite into graphene)
In conclusion, producing graphene from graphite using CVD is a relatively simple process that requires only basic equipment and some knowledge of chemistry. With advances in materials science and technology, we can expect to see more applications of graphene in the future, making it a promising material for a wide range of industries.
Inquiry us