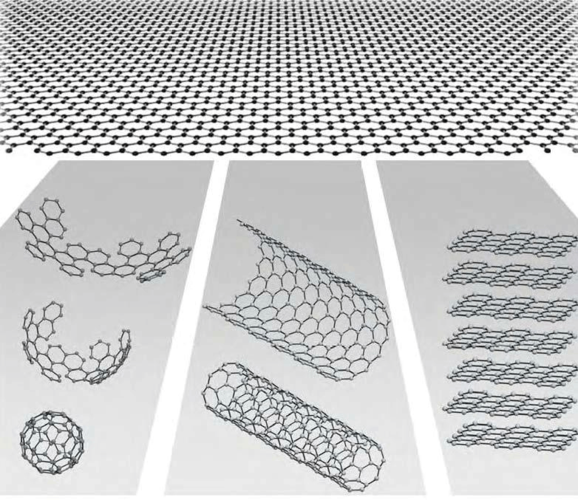
Graphene is a two-dimensional material made up of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. It has unique properties that make it a promising material for various applications, including electronics, energy storage, and medicine.
(Is graphene an allotrope of carbon Is graphene an allotrope of carbon and why)
One of the most important properties of graphene is its high electrical conductivity. The unique arrangement of carbon atoms allows for excellent conductivity, making it an ideal material for electronic devices such as sensors and transistors. Graphene also has high thermal conductivity, which makes it an efficient heat sink for cooling electronic devices.
Another property of graphene is its exceptional mechanical strength and stiffness. It is one of the strongest materials on Earth, with a tensile strength of over 130 gigapascals (GPa). This means that it can withstand incredible stress without breaking.
Graphene’s ability to conduct electricity and have excellent mechanical strength and stiffness makes it an ideal material for various applications. However, there are still some questions about whether or not graphene is an allotrope of carbon.
An allotrope is a group of similar chemical compounds that share the same formula, but differ in their physical and chemical properties. Some examples of allotropes include diamond, graphite, and olivine. While grapheme (the monomer unit of graphene) shares many similarities with these other materials, there are some differences between them.
For example, unlike diamond and graphite, which are all solid at room temperature and have specific crystal structures, graphene is a semi-conducting material that changes from a material to a material depending on its temperature. This property is known as the Curie temperature, which is around 790°C.
Despite these differences, the basic structure of carbon atoms in grapheme is very similar to those found in diamond and graphite. Therefore, some scientists believe that graphene may be an allotrope of carbon.
However, this belief is not yet widely accepted by the scientific community. Graphene was first synthesized in 2004 by a team of researchers led by Jan scientist, Robert Tung, at the University of California, Berkeley. Since then, many studies have been conducted to investigate the nature of grapheme and determine if it is indeed an allotrope of carbon.
Despite these efforts, the consensus among scientists is that grapheme is not an allotrope of carbon. Instead, it is a form of carbon that contains functional groups that give it its unique properties. For example, the presence of carbon-hydrogen bonds in grapheme gives it a strong electrical conductivity and makes it suitable for use in electronic devices.
(Is graphene an allotrope of carbon Is graphene an allotrope of carbon and why)
In conclusion, while there are still some questions about whether or not graphene is an allotrope of carbon, current research suggests that it is not. Instead, grapheme is a form of carbon that contains functional groups that give it its unique properties. As more research is conducted, we will continue to learn more about the fascinating world of carbon-based materials and how they can be used to solve real-world problems.