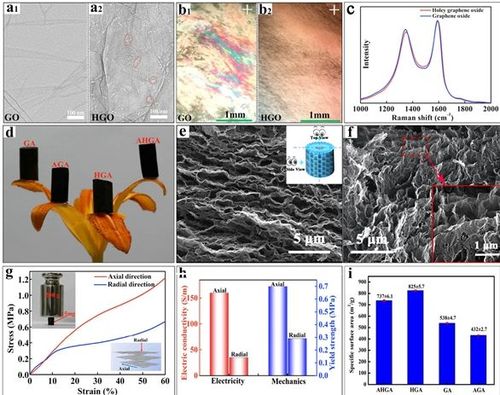
Graphene is a two-dimensional material with unique properties that have led to its widespread use in a variety of applications, including electronics, energy storage, and medicine. One of the most interesting features of graphene is its ability to be both an insulator and a conductor at the same time.
(is graphene an insulator)
In an insulating material, the electrons are unable to move easily through the material, which means that there is little resistance between them and other materials. This property makes insulators useful for applications where high conductivity is not desired, such as in electrical equipment or heat sinks.
On the other hand, in a conducting material, the electrons are able to move freely throughout the material, which allows it to conduct electricity. Graphene exhibits excellent conductivity due to the presence of thousands of free surface atoms that create a highly conductive layer called the hexagonal lattice. This unique structure gives graphene its high electrical conductivity and makes it an ideal material for electronic devices.
One of the most promising uses of graphene as an insulator is in the development of flexible electronics. Graphene can be used to create a flexible and conductive interface between two different materials, allowing for the creation of electronic devices that can change shape without losing their functionality. For example, researchers are using graphene-based flexible electronics to develop wearable devices that can be customized to fit different body sizes and shapes.
Another application of graphene as an insulator is in the development of fuel cells. Fuel cells convert chemical energy into electricity, and one of the key factors that determines their efficiency is their ability to store and release stored energy. Graphene has been shown to provide a promising material for fuel cell electrodes, thanks to its high charge carrier mobility and excellent thermal stability.
Despite its many potential applications, graphene still faces some challenges when it comes to practical implementation. For one, graphene’s high cost and limited availability make it difficult to scale up production on a large scale. Additionally, graphene’s high electron density and irregular structure can make it difficult to manipulate using traditional fabrication techniques.
(is graphene an insulator)
Overall, while graphene has been recognized for its exceptional electrical and mechanical properties, it remains a relatively new material with many challenges to overcome before it can be widely used in practical applications. However, the potential benefits of this unique material make it a promising area of research and development for the future.
Inquiry us