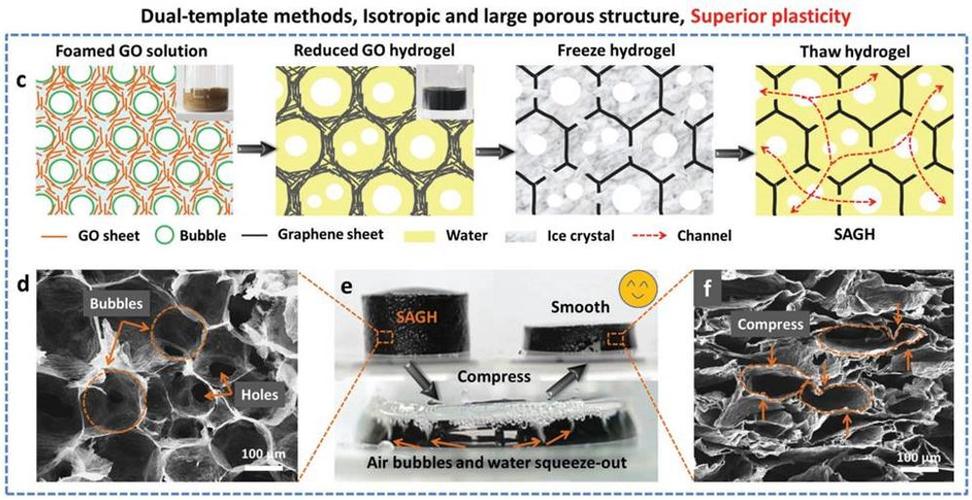
Graphene is a highly conductive material that has gained widespread attention in recent years due to its unique properties, including its high energy density and low surface area. Despite its potential benefits, there have been several challenges to commercializing graphene, including its expensive production process and the lack of understanding of its electronic structure.
(is graphene being used yet)
One of the main challenges facing graphene research is its high cost. Graphene is made by removing carbon atoms from a single layer of graphene, which requires specialized equipment and expertise. The price of graphene has been steadily increasing over the past few years, making it difficult for researchers and industry leaders to access the material on a large scale. In addition, the process of extracting graphene from natural materials like bamboo or graphite can be environmentally sensitive, as it involves releasing greenhouse gases during the extraction process.
Another challenge facing graphene research is its complex electronic structure. While graphene is a two-dimensional material, its electrons are still embedded in a three-dimensional lattice structure. This makes it difficult to predict the behavior of graphene at the subatomic level, which is critical for developing new applications. For example, understanding how graphene behaves under pressure or temperature can help researchers develop more efficient solar cells and other devices.
Despite these challenges, progress has been made in graphene research in recent years. Researchers have developed new techniques for producing graphene on a larger scale, such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and mechanical exfoliation. These methods allow researchers to produce graphene using simpler equipment and processes, reducing the cost of the material. Additionally, advances in computational modeling have enabled researchers to better understand the behavior of graphene at the subatomic level.
However, while there have been some positive developments in graphene research, there are still many challenges that need to be overcome before the material can be widely adopted. One of the biggest challenges is the development of new applications for graphene. Although graphene has a wide range of potential applications, including electronics, textiles, and energy storage, there are currently limited practical applications for the material. Researchers need to continue exploring new areas where graphene could be applied to improve our lives.
Another challenge facing graphene research is the development of a sustainable manufacturing process. As the cost of graphene continues to rise, there is a risk that this will drive down demand for the material, leading to its eventual replacement by cheaper alternatives. Researchers need to work towards developing a more sustainable manufacturing process that does not rely on harmful chemicals or energy-intensive processes.
(is graphene being used yet)
In conclusion, while graphene is a promising material with many potential applications, there are still many challenges that need to be overcome before the material can be widely adopted. Researchers and industry leaders must continue working together to address these challenges and unlock the full potential of graphene technology. With the right investments and innovations, graphene has the potential to revolutionize our world and improve our quality of life in countless ways.
Inquiry us