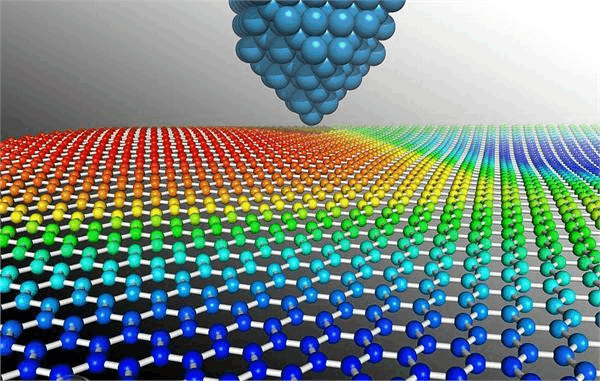
Graphene is a unique material that has revolutionized the field of materials science due to its exceptional electronic, mechanical, and thermal properties. One of the key features of graphene is its unique electron density distribution, which leads to an attractive electric field.
(what are modes in graphene)
One of the most well-known forms of graphene is hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), which consists of six layers of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. h-BN exhibits excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for use in electronics and energy storage applications. Additionally, it is strong, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion.
Another form of graphene is face-centered cubic (FCC) graphene, which consists of four layers of carbon atoms arranged in a face-centered cubic lattice. FCC graphene has a higher surface area than h-BN, which makes it more suitable for use in batteries and other electronic devices.
Graphene also has a unique chemical behavior that allows it to form new materials by chemical reduction. For example, one type of graphene oxide, which is formed from the reaction of graphene with oxygen, can be used as a catalyst for chemical reactions.
(what are modes in graphene)
Overall, graphene has many potential uses in various fields, including electronics, energy storage, and catalysis. As researchers continue to study the properties of graphene, we can expect to see even more innovative uses in the future.
Inquiry us