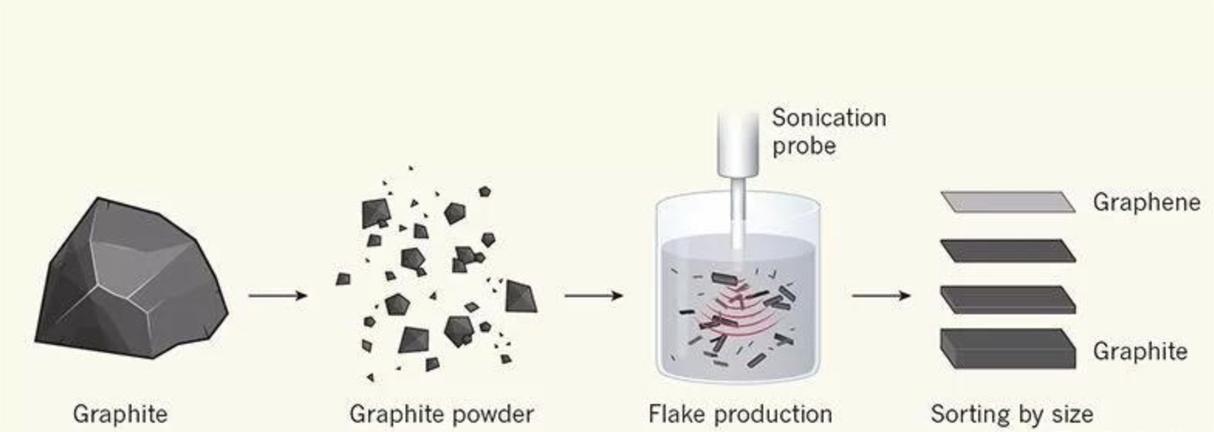
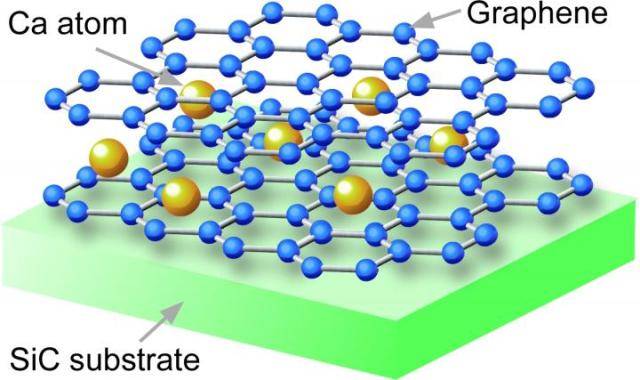
Graphene oxide (GO) is a materials science material that has gained significant attention due to its unique properties and potential applications in various fields. It is a single-layered two-dimensional carbon sheet with a high surface area, making it an ideal material for electronic devices and energy storage.
(where is graphene oxide used)
One of the most promising applications of graphene oxide is in the development of energy storage systems. Graphene oxide can be used as an electrode material in batteries or supercapacitors to store energy. This makes it a useful alternative to traditional battery technologies such as lithium-ion batteries, which have limited capacity and high cost.
Another application of graphene oxide is in the production of fuel cells. The high surface area of graphene oxide allows for better contact between the fuel and the catalyst, improving the efficiency and reducing the amount of reactants needed to produce electricity.
Graphene oxide is also being studied as a possible carrier material for quantum computing. The large surface area of graphene oxide provides more pathways for electrons to move through the material, which could make it easier to manipulate and control qubits.
In addition, graphene oxide is being explored as a material for use in water purification and desalination. Its high surface area and ability to adsorb contaminants make it a promising material for these applications.
Despite its many potential applications, graphene oxide faces several challenges in its development. One of the biggest challenges is the stability of the material, particularly at high temperatures. Graphene oxide can be easily degraded by heat, which could limit its use in certain applications.
Another challenge is the scalability of graphene oxide production. Currently, the cost of producing graphene oxide is relatively high, which limits its widespread adoption.
Despite these challenges, researchers continue to work on developing new ways to improve the stability and scalability of graphene oxide production. For example, some researchers are exploring the use of microwave heating to improve the thermal stability of graphene oxide.
(where is graphene oxide used)
Overall, graphene oxide holds great promise for many different applications in technology and sustainability. As researchers continue to develop new methods to improve the stability and scalability of graphene oxide production, we can expect to see it increasingly used in a variety of applications in the future.
Inquiry us